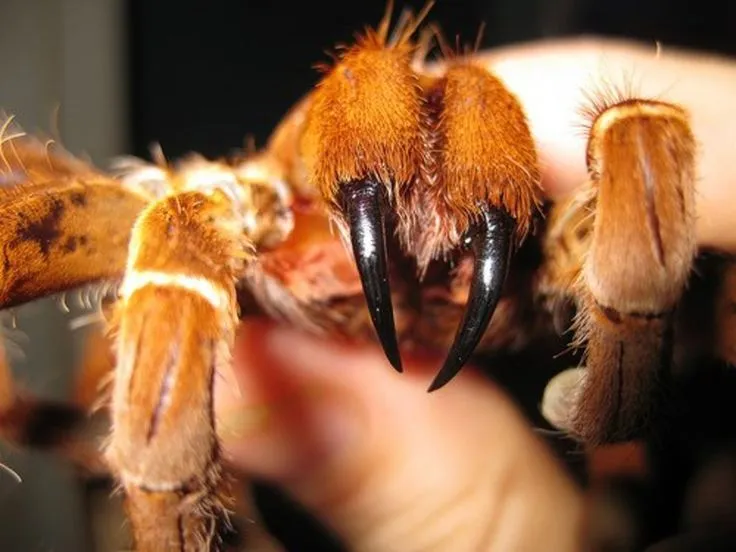
The Reality of Tarantula Bites
Tarantulas, with their imposing size and often hairy appearance, are a source of both fascination and fear. One of the most common questions surrounding these arachnids is whether their bites are deadly. While the image of a venomous spider can conjure up images of severe danger, the reality is often more nuanced. This article will delve into the facts surrounding tarantula bites, providing a clear understanding of the risks involved and separating fact from fiction. It’s crucial to approach this topic with accurate information, dispelling myths and offering practical advice for anyone who may encounter these spiders.
Fact 1 Toxicity Levels
The toxicity of tarantula venom is a critical factor in determining the severity of a bite. Unlike some spiders with highly potent venom, tarantulas generally possess venom that is not considered lethal to humans. The primary components of tarantula venom include various enzymes and proteins, which are designed to immobilize their prey, such as insects, small reptiles, or mammals. However, the potency of this venom is typically not strong enough to cause severe systemic effects in humans. Understanding the composition of the venom helps clarify why the risk of fatality is significantly lower than it might be with other venomous creatures.
Venom Composition and Effects

Tarantula venom contains a complex mix of compounds, including neurotoxins and enzymes. These substances work to disrupt the nervous system of the spider’s prey, causing paralysis. In humans, the effects are usually much milder. Common symptoms of a tarantula bite may include localized pain, redness, swelling, and itching at the bite site. In rare cases, more severe reactions like muscle cramps or nausea might occur. The specific composition can vary slightly between different species of tarantulas, but the general effect is similar: an uncomfortable experience rather than a life-threatening event.
Impact of Bite on Humans
For most people, a tarantula bite results in minor, localized symptoms. The venom’s effect is often compared to a bee sting. The primary discomfort comes from the physical trauma of the bite itself, rather than the venom’s toxicity. There might be some initial sharp pain, followed by inflammation and itching. The duration of these symptoms is usually short-lived, typically resolving within a few days to a week. However, the experience can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the species of tarantula involved, making it crucial to understand the range of possible reactions.
Fact 2 Allergic Reactions
While the venom itself is not highly toxic, allergic reactions can occur in some individuals. These reactions can range from mild to severe, and it’s important to be aware of the potential risks. Allergic responses are caused by the body’s immune system reacting to the foreign proteins in the venom. It’s essential to identify these signs and seek medical attention if necessary, as they can escalate quickly. The possibility of an allergic reaction adds a layer of complexity to assessing the danger of a tarantula bite, underscoring the need for careful monitoring and prompt response.
Symptoms of Allergic Response

Symptoms of an allergic reaction to a tarantula bite can manifest in several ways. Mild reactions might include increased swelling, redness spreading beyond the bite site, and hives. More severe reactions can involve difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat. These symptoms indicate a more serious allergic response, which requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing these signs is crucial for ensuring timely intervention and preventing the reaction from becoming life-threatening. The diversity of potential reactions underscores the importance of individual awareness and preparedness.
Severity of Allergic Reactions
The severity of allergic reactions varies greatly from person to person. Some individuals experience mild discomfort, while others may face life-threatening conditions like anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that can cause the airways to constrict, leading to difficulty breathing and potentially death. Prompt treatment with epinephrine (an EpiPen) and other medical interventions is crucial in managing anaphylaxis. The unpredictability of allergic reactions highlights the need for medical professionals to be ready for any patient experiencing the bite.
Fact 3 Bite Location & Type
The location and type of the bite can influence the experience and outcome. Bites on sensitive areas, such as the face or neck, might cause more swelling and discomfort than bites on the limbs. The way a tarantula bites—whether it’s a single bite or multiple bites—can also affect the severity of the local reaction. Understanding these variations helps in assessing the potential impact and determining the appropriate course of action. Variations can be quite significant, and understanding them is key to risk management.
Variations Based on Tarantula Species
Different species of tarantulas have varying levels of venom potency and fang size. Larger tarantulas may deliver more venom due to their size, but this doesn’t necessarily equate to higher toxicity. Some species have more irritating hairs, which can cause skin irritation and discomfort, even if they don’t bite. The geographical origin of the tarantula can also affect the venom’s composition. Learning about the specific type of tarantula involved in a bite is critical in predicting the potential impact and ensuring appropriate treatment measures. The species matters significantly when assessing the level of risk.
Differences in Bite Severity
The severity of a bite is determined by multiple factors, including the amount of venom injected, the individual’s sensitivity, and the bite location. A bite on an area with a rich blood supply, such as the face, might show symptoms faster than a bite on a limb. In rare instances, multiple bites can lead to a more pronounced reaction. Understanding these factors is important in evaluating the potential risks. This evaluation allows for appropriate steps and helps prevent unnecessary concerns.
Fact 4 First Aid and Treatment
Knowing what to do immediately after a tarantula bite can significantly affect the outcome. The primary goal is to minimize the venom’s impact and reduce discomfort. Prompt action and effective first aid are crucial for managing the situation effectively. It is important to remain calm and take appropriate steps to ensure safety.
Immediate Steps After a Bite

The immediate steps after a tarantula bite should include: keeping calm, gently cleaning the bite area with soap and water, and applying a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain. It’s important to elevate the affected limb to reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain. Monitoring for signs of allergic reaction is crucial; if any symptoms appear, seek medical attention immediately. Document the event, including the time, location, and type of spider if possible. All of these steps enhance the potential for recovery.
Medical Treatment Options
Medical treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the bite and any allergic reactions. Doctors might administer antihistamines or corticosteroids to control allergic responses. In severe cases of anaphylaxis, epinephrine injections are critical. Medical professionals can also provide pain relief and manage any complications that arise. Antibiotics might be prescribed if the bite site becomes infected. Close monitoring and appropriate medical intervention are vital for ensuring a positive outcome, especially when dealing with serious allergic reactions or complications.
Fact 5 Mortality Rate
The mortality rate from tarantula bites is extremely low. Deaths directly attributable to tarantula bites are exceedingly rare, making it statistically insignificant. This underscores the point that, while bites can be unpleasant, they are generally not life-threatening to humans. Understanding the low risk of fatalities provides essential context, mitigating unnecessary fear and anxiety about encounters with tarantulas. Knowing the mortality rate helps to put the level of danger in perspective.
Historical Data on Fatalities

Historical data and scientific literature confirm the rarity of tarantula bite fatalities. There have been very few, if any, documented cases of human deaths directly caused by tarantula venom. Most reported cases involve secondary infections or complications arising from allergic reactions. These data show that the primary risk comes from allergic responses rather than the venom’s toxicity itself. These statistics support the conclusion that, for most people, a tarantula bite does not pose a severe threat.
Factors Contributing to Survival
Several factors contribute to the high survival rate following tarantula bites. These include the relatively low toxicity of the venom, the availability of effective medical treatments for allergic reactions, and the prompt response to bite incidents. Also, the generally robust health of the average human and the lack of severe systemic effects from the venom add to the favorable outcomes. The combination of these factors ensures that the vast majority of people fully recover from tarantula bites with minimal complications. Timely first aid and access to medical care further enhance these outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while a tarantula bite can be a painful and unpleasant experience, it is rarely deadly to humans. The venom is generally not highly toxic, and most people experience only localized symptoms. The main risks come from allergic reactions, which can vary in severity. Knowing the appropriate first aid measures and seeking medical attention if needed is essential. The low mortality rate and the effectiveness of medical treatments provide reassurance. When dealing with tarantulas, it is important to be aware of the potential risks but to maintain a balanced perspective based on accurate information and proper precautions. Staying informed and taking the right actions will help ensure a safe encounter with these fascinating creatures.
