Embarking on the journey of building your own Tarantula 3D printer can be an incredibly rewarding experience. It’s a chance to delve into the fascinating world of 3D printing, understand how these machines function, and customize your own printing experience. This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through the process, from understanding the components to your first successful print. Building a Tarantula 3D printer allows you to create a machine tailored to your specific needs, experiment with different materials, and even troubleshoot and repair it yourself. Prepare to unlock the potential of 3D printing and bring your ideas to life.
What is a Tarantula 3D Printer?
The Tarantula 3D printer is a popular and affordable open-source 3D printer kit. It’s known for being a great entry point into the world of 3D printing because it offers a balance of affordability, functionality, and community support. Many hobbyists choose the Tarantula because it’s a relatively straightforward build, provides good print quality, and allows users to learn about the inner workings of 3D printing technology. The Tarantula is typically based on the Prusa i3 design, offering a sturdy frame and the ability to print a variety of materials. This makes it an excellent choice for both beginners and those looking to expand their 3D printing knowledge.
Components of a Tarantula 3D Printer
A Tarantula 3D printer consists of several key components working in harmony. You’ll find a sturdy frame, often made of aluminum extrusions, to provide stability. The X, Y, and Z axes are moved with stepper motors that control the movement of the print head and the bed. A heated bed allows you to print with materials like ABS and PETG that require a heated surface to adhere properly. The extruder melts and feeds the filament through a nozzle onto the build plate. The control board acts as the brain, interpreting G-code instructions and controlling all aspects of the printer’s operation. Limit switches (endstops) ensure that the printer knows the boundaries of its movement. Power supply provides the necessary electricity. Finally, a spool holder to keep the filament readily available.
Understanding these components is critical, as this will make your building experience so much better. You can get a full understanding of the whole printing mechanism.
Frame and Base Assembly
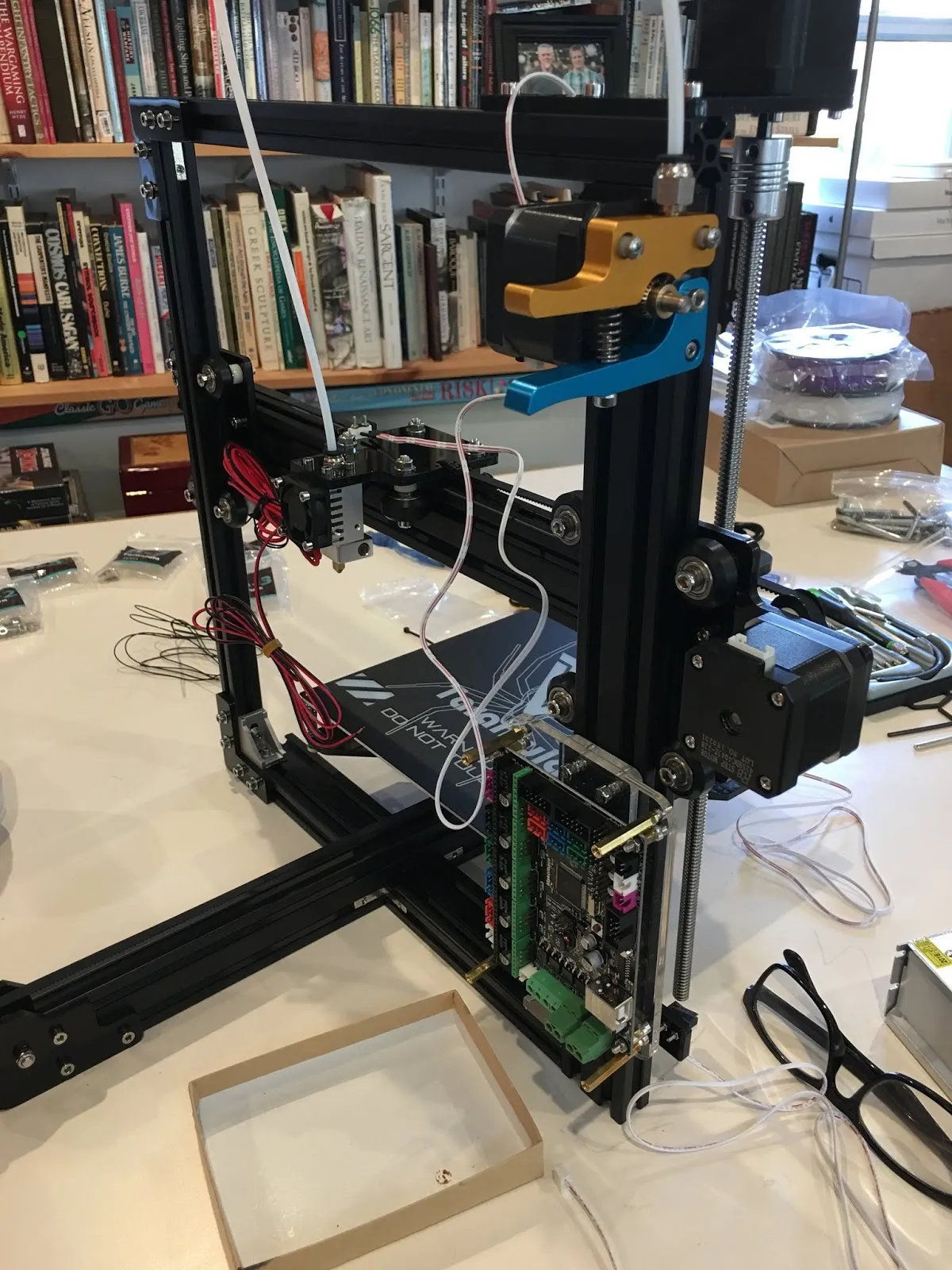
The frame is the foundation of your 3D printer. It is commonly made from aluminum extrusions and provides the structure needed for all other parts. Begin by identifying all the frame pieces, often provided in a kit with pre-cut lengths. Connect the frame components using the provided screws, brackets, and corner pieces, ensuring that the frame is square and level. This step is crucial for print quality, because any misalignment here can cause problems later on. Double-check your work by using a level to ensure that the frame is stable and that the printer won’t rock when printing. Tighten all screws securely, but avoid over-tightening, which could damage the extrusions. Once assembled, the frame should be rigid and ready to support the other components.
Installing the X, Y, and Z Axes
The axes are the heart of your 3D printer’s movement system. Proper installation of these components is essential for precise and accurate prints. The X-axis controls the horizontal movement of the print head, the Y-axis controls the bed’s back-and-forth motion, and the Z-axis moves the print head vertically. Each axis will need a motor, belts, and pulleys to make it move properly. Ensure smooth movement of all axes by checking the belts and the linear bearings. Any obstruction or stiffness in the movement can lead to print defects. Follow the instructions provided with your kit carefully, paying close attention to the order of assembly and the placement of components. Take your time and be patient, as precision in this step will pay off in the long run.
X-Axis Assembly
The X-axis is where the print head moves. Attach the X-axis carriage to the linear bearings, making sure they slide smoothly along the X-axis rods. Secure the print head mount to the carriage, being sure it’s aligned correctly. Install the X-axis motor and pulley, ensuring the belt tension is correct. Over-tensioning can damage the motor or bearings, and under-tensioning can cause slippage and print errors. The X-axis belt should be tight enough to prevent slipping but loose enough to allow smooth movement. Double-check the belt path and ensure that the print head moves freely along the entire length of the X-axis. Carefully connect any wiring for the print head components, such as the hotend fan and the thermistor.
Y-Axis Assembly
The Y-axis controls the movement of the print bed. Mount the Y-axis rails or rods to the printer frame, making certain they are parallel and properly aligned. Attach the Y-axis motor and pulley, setting the belt tension. Place the print bed on the Y-axis carriage. Check for smooth movement and even support across the entire bed surface. Ensure the belt runs straight and doesn’t rub against any components. When the Y-axis moves, make sure the bed travels in a straight line without any wobbling or binding. If there are any issues, readjust the rods or tighten the belts as necessary.
Z-Axis Assembly
The Z-axis is responsible for the vertical movement of the print head. Securely attach the Z-axis leadscrews to the frame. The leadscrews should be aligned and move freely. Attach the Z-axis motor(s) and any couplers needed to connect them to the leadscrews. The print head carriage will move up and down as the leadscrews rotate. Ensure that the Z-axis carriage moves smoothly and does not bind. Verify the stability of the Z-axis to prevent any wobbling or instability during printing, as this can impact layer adhesion and print quality.
Wiring the Electronics
Proper wiring is vital for the safe and proper functioning of your 3D printer. Begin by carefully studying the wiring diagram provided with your kit. Connect the stepper motors to the control board, paying attention to the correct wiring order. Wire the endstops to their designated pins on the control board. Connect the heated bed and the hotend to the appropriate terminals, ensuring they are secure and making a good connection. Double-check all wiring connections for polarity and secure fit. Use wire ties or cable management to keep the wires neat and organized, preventing them from interfering with moving parts. Be patient and meticulous when wiring, and always consult the wiring diagram if you are unsure about a connection.
Connecting the Motors
Stepper motors are critical for the accurate movement of the printer’s axes. The motors will be labeled (X, Y, Z, and E for the extruder). Refer to your control board’s documentation to identify the motor driver pins. Firmly plug the motor wires into the control board. The order of the wires in the connector matters, and if they’re reversed, the motor may not function correctly. After connecting the motors, test each axis to ensure it moves in the correct direction. If a motor moves in the wrong direction, you might need to reverse the wiring or make an adjustment in the firmware. Listen to make sure the motors run smoothly without any unusual noises, which could indicate a mechanical issue.
Connecting the Endstops
Endstops are small switches that tell the printer when an axis has reached its limit. Endstops are usually mounted on the frame and will trigger when the print head or bed touches them. Wiring the endstops properly is essential for safety and to ensure the printer knows its boundaries. Locate the endstop connectors on the control board and connect the endstop switches to the appropriate pins. Make sure the endstops are positioned correctly so they trigger at the end of each axis’s travel. Once connected, test each endstop to verify that it is working correctly. The endstops will protect your machine from crashes and limit movement.
Connecting the Heated Bed and Extruder
The heated bed and extruder are essential for printing certain materials. Attach the heated bed to the Y-axis carriage and connect it to the control board. Make sure the wires are securely connected. Connect the extruder’s heating element and thermistor to the control board. Make sure the wires are not touching the hot parts of the extruder. Double-check all connections to make sure everything is in good order and that there is no chance of a short circuit. If you aren’t comfortable with wiring, get assistance from someone who has electrical knowledge.
Firmware Installation and Configuration
Firmware is the software that controls the 3D printer’s behavior. It tells the printer how to move, heat, and extrude. The most popular firmware is Marlin. You will need to download the Marlin firmware from the official Marlin website. You’ll also need to download the Arduino IDE, which is used to upload the firmware. After installing both, you need to configure the firmware for your printer’s specific hardware. Make adjustments like the printer’s size, the type of hotend, and the thermistor type. Once configured, compile the firmware using the Arduino IDE, this turns the code into a format the printer can understand.
Uploading Firmware
Connect your 3D printer’s control board to your computer via a USB cable. Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct board and port for your printer. Click the upload button and wait for the process to complete. If there are any errors during the upload, go back and review the instructions, check your configuration, and make sure the board is properly connected. This will usually fix most of the errors. Once the upload is complete, the firmware is installed and the printer is ready to be used. You may need to reset the printer to initiate the new firmware.
Configuring the Firmware
After uploading the firmware, you will need to configure it to match your printer’s specifications. This will involve changing some of the settings in the firmware to match your hardware. Use a program like Pronterface or Repetier-Host to send G-code commands. You can use these to make sure the motors are working correctly, the endstops are working correctly, and the temperature sensors are reading correctly. This step will allow you to create a functional printer, specific to your design.
Calibration and Testing
Calibration is an important step to ensure the printer works well. Level the bed, calibrate the extruder and check the firmware settings. These are the most important steps for calibrating your printer. Proper calibration leads to high-quality prints and reduces print defects. Take your time, follow the instructions carefully, and run test prints as needed to refine your settings. Be patient and persistent. It’s all worth it when you finally get your first perfect print.
Leveling the Bed
Bed leveling is one of the most critical steps in 3D printing. If the bed is not level, the first layer of your print will not adhere properly. This is what causes the print to fail. Place a piece of paper between the nozzle and the bed and adjust the bed leveling screws or knobs until the nozzle lightly grips the paper. Repeat this process at all four corners of the bed. Fine-tune the leveling by adjusting the screws in small increments. Once the bed is level, perform a test print of a single-layer square or a bed leveling test pattern to verify the level. If the nozzle is too close to the bed, the filament will not extrude properly. If the nozzle is too far, the filament will not adhere. Adjust and repeat until you get a perfect first layer.
Calibrating the Extruder
Extruder calibration ensures that the printer extrudes the correct amount of filament. Measure and mark a known length of filament, usually 100 mm, from the extruder’s inlet. Heat the hotend to its printing temperature and extrude a small amount of filament. Then, extrude the marked length of filament and measure how much has actually been extruded. If the extruder is not extruding the right amount, adjust the steps per mm setting in the firmware. You can find the correct setting by calculating the distance extruded divided by the distance requested. Repeat these steps until you achieve the precise extrusion needed for high-quality prints.
First Print and Troubleshooting
After completing the assembly and calibration, it’s time to print your first model! Start by downloading a test print, such as a calibration cube, from the internet. Load the model into a slicing program like Cura or PrusaSlicer. These programs will convert the 3D model into G-code, which the printer will use to move the print head and bed. Ensure the settings in the slicing program are correct for your printer and the filament you are using. Once you have the G-code file, load it onto your printer via an SD card or USB connection. Monitor the first layer of the print closely to make sure the filament adheres properly. If you encounter any issues, refer to the troubleshooting guide or the community.
Troubleshooting is an important part of the 3D printing process. Common problems include poor bed adhesion, warping, or nozzle clogs. If you have adhesion problems, try using glue or a heated bed. If the print is warping, adjust the bed temperature and/or enclose the printer. If the nozzle is clogged, you can try using a needle to unclog it, or replacing the nozzle. The 3D printing community is a valuable resource. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you’re having trouble. With some patience and persistence, you’ll be printing amazing models in no time.
