What to Do Immediately After a Tarantula Bite
Encountering a tarantula bite can be a frightening experience, but knowing how to respond quickly can significantly impact your recovery. The initial minutes are critical in minimizing the effects of the bite. Your immediate actions will set the stage for effective treatment and reduce the likelihood of complications. Staying calm and following a systematic approach ensures you address the situation efficiently. Remember, while tarantula bites are rarely life-threatening to humans, they can cause significant discomfort and, in rare cases, trigger allergic reactions. Therefore, rapid and appropriate first aid is paramount. The primary goal at this stage is to mitigate the immediate impact of the venom and prevent secondary issues like infection. By being proactive, you can ensure a smoother recovery and a return to normal as quickly as possible.
Assess the Bite Site
Immediately after a tarantula bite, the first step is to assess the bite site. This involves carefully looking at the area to determine where the bite occurred and the extent of the injury. Look for visible puncture marks, which may appear as small, pinpoint holes. Note any signs of swelling or redness, which are common indicators of a reaction to the venom. Gentle palpation of the area can help identify tenderness or pain. Additionally, observe for any presence of hairs from the tarantula, which might have become embedded in the skin. This assessment also includes checking for any other physical symptoms, such as changes in skin temperature or the development of blisters. Documenting these initial observations will be useful for further treatment and for informing medical professionals if necessary. A thorough evaluation helps in selecting the right course of action and in monitoring the progression of the bite’s effects.
Clean the Wound

After assessing the bite, the next important step is to clean the wound thoroughly. This helps to remove any venom residue and minimize the risk of infection. Use mild soap and water to gently wash the affected area. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scrubbing vigorously, as this can irritate the skin and potentially spread the venom. Rinse the area well to ensure all traces of soap are removed. Pat the area dry with a clean towel. If you have access to an antiseptic solution, like diluted povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, apply it to the bite site after cleaning. This will further help to disinfect the wound. However, avoid alcohol-based products, as they can dry out the skin and cause further irritation. Keeping the wound clean is essential for preventing bacterial infections and promoting faster healing, making it a critical step in managing a tarantula bite.
Apply Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress is a simple yet effective way to manage pain and reduce swelling after a tarantula bite. Use an ice pack or a cold compress wrapped in a cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin, which could cause frostbite. Apply the cold compress to the bite site for 10 to 15 minutes at a time, repeating this every hour as needed. The cold helps to constrict blood vessels, which can slow down the spread of venom and lessen inflammation. It also provides a numbing effect, which can alleviate pain and discomfort. Make sure to monitor the skin for any adverse reactions to the cold, such as excessive redness or blistering. If these occur, discontinue the use of the cold compress and consult with a medical professional. Combining a cold compress with other first aid measures can provide significant relief and promote a quicker recovery from the bite.
Seek Medical Attention
While tarantula bites are generally not life-threatening, seeking medical attention is a crucial step, especially if symptoms worsen or if the individual has any known allergies. Contacting a healthcare provider or visiting an urgent care facility ensures proper evaluation and treatment. Medical professionals can assess the severity of the bite and provide necessary interventions, such as pain relief medication, antihistamines to manage allergic reactions, or antibiotics to treat potential infections. They can also provide guidance on wound care and monitor for any complications. Do not hesitate to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or any signs of an allergic reaction. Even if symptoms appear mild initially, it is best to consult a medical professional to rule out any serious complications and to ensure proper management of the bite. Early medical intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term problems.
Identifying Tarantula Bite Symptoms

Understanding the symptoms of a tarantula bite is crucial for effective management and timely medical intervention. Recognizing the specific signs and symptoms allows for an informed response and can help distinguish between a mild reaction and a more severe one. The range of symptoms can vary widely, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the specific type of tarantula involved. Knowing what to look for enables you to assess the severity of the bite and take the necessary steps to seek medical attention if needed. The following sections will provide detailed information on the various symptoms that may occur after a tarantula bite, helping you to be better prepared to handle the situation.
Localized Pain and Swelling
Localized pain and swelling are common initial symptoms of a tarantula bite. The intensity of the pain can vary from mild discomfort to a sharp, stinging sensation, depending on the sensitivity of the individual and the amount of venom injected. Swelling typically occurs around the bite site and may extend to the surrounding tissues. This swelling is a result of the body’s inflammatory response to the venom. In most cases, the pain and swelling are localized and subside within a few hours to a few days. However, it’s important to monitor these symptoms for any worsening signs. If the pain becomes unbearable, the swelling increases significantly, or other symptoms such as fever or chills develop, medical attention should be sought immediately. The assessment of pain and swelling helps to determine the need for further treatment and to rule out more severe complications.
Redness and Itching
Redness and itching are also typical symptoms associated with a tarantula bite. The redness, or erythema, is caused by the dilation of blood vessels in the area, a part of the inflammatory response to the venom. The itching, or pruritus, can range from mild to intense and can be quite bothersome. This is often due to the release of histamine and other chemicals by the body in response to the bite. Itching can cause a strong urge to scratch, which can irritate the skin and potentially lead to infection. It’s important to avoid scratching the bite site, as this can worsen the symptoms and prolong healing. Applying a cold compress and using anti-itch creams, as recommended by a healthcare professional, can provide relief. Monitoring the redness and itching can also help in assessing the progress of the bite. If the redness and itching worsen or spread, it’s advisable to seek medical attention.
Muscle Cramps
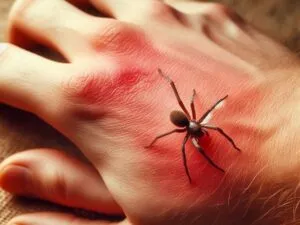
In some cases, tarantula bites can lead to muscle cramps, although this is less common than localized pain, swelling, redness, and itching. Muscle cramps can occur as a result of the venom’s effects on the nervous system or the body’s response to the bite. These cramps can manifest as involuntary muscle contractions, often causing significant discomfort. The affected muscles may feel tight, and the pain can range from mild to severe. If muscle cramps develop, it is crucial to stay hydrated, as dehydration can exacerbate the issue. Gentle stretching and rest may help to alleviate the cramps, but medical attention should be sought if they are severe or persistent. Healthcare professionals can provide specific treatments to manage the cramps and minimize discomfort. Monitoring the occurrence and severity of muscle cramps is important to assess the bite’s impact and ensure appropriate medical intervention is provided.
Severe Reactions
Although rare, severe reactions can occur after a tarantula bite, and it’s essential to be aware of these potential complications. The most severe reaction is an allergic reaction, which can manifest with symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, hives, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat. These symptoms require immediate medical attention, as they can be life-threatening. Another serious concern is infection at the bite site, which can lead to symptoms like increased pain, swelling, redness, pus, and fever. If any signs of infection are observed, medical intervention is necessary to prevent the spread of infection. In extremely rare instances, venom from certain tarantulas can cause more severe systemic effects, such as neurological symptoms. Any person experiencing significant or unusual symptoms after a tarantula bite should seek immediate medical assistance. Quick medical intervention can make a significant difference in reducing the risks of severe reactions and ensuring the best possible outcome.
How to Care for a Tarantula Bite at Home
After receiving initial first aid and, if necessary, medical care, caring for a tarantula bite at home involves several steps to promote healing and manage symptoms. This ongoing care is crucial for ensuring a full recovery and preventing complications. Implementing these home care strategies will help to alleviate discomfort, minimize swelling, and reduce the risk of infection. However, it is important to follow all the advice provided by a medical professional and seek further medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. The following sections will provide an overview of effective at-home care measures.
Pain Management Techniques

Pain management is a key component of home care for a tarantula bite. Several methods can be employed to reduce pain and increase comfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be used to manage mild to moderate pain. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions on the product label. Applying a cold compress to the bite site can also help to numb the area and reduce pain and swelling. For more severe pain, a doctor may prescribe stronger pain relief medication. Avoid using heat on the bite site, as it can increase swelling and discomfort. Additionally, keeping the affected limb elevated can help to reduce swelling and pain. Remember to consult with your doctor if you are unsure about which pain relief options are best for you, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Managing Swelling and Itching
Managing swelling and itching are essential for comfort and healing. To reduce swelling, continue to apply a cold compress for 10 to 15 minutes every few hours. Elevating the affected limb above heart level can also help to reduce fluid buildup and promote healing. To manage itching, avoid scratching the bite site, as this can exacerbate the irritation and increase the risk of infection. Over-the-counter anti-itch creams containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or calamine lotion can provide relief. If the itching is severe, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications. Keep the bite site clean and dry to minimize the risk of infection. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is generally sufficient. Avoid using harsh chemicals or strong soaps, as these can irritate the skin and worsen itching. Proper management of swelling and itching can significantly improve the healing process and the overall comfort level.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for managing a tarantula bite effectively. While many bites can be managed with at-home care, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Prompt intervention can prevent complications and improve the outcome of the bite. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s essential to seek professional medical advice immediately. These are indicators that the bite may be more severe or that the body is reacting in an atypical manner. The following sections will describe the critical signs that require immediate medical evaluation.
Signs of Allergic Reaction

Signs of an allergic reaction require immediate medical attention because they can quickly become life-threatening. Allergic reactions indicate that the body is overreacting to the venom, leading to a variety of potentially dangerous symptoms. One of the most concerning symptoms is difficulty breathing, which could lead to respiratory arrest. Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat is another serious sign, as it can obstruct the airway. Hives or a widespread rash, often accompanied by itching, can also indicate an allergic response. Dizziness or lightheadedness, potentially leading to loss of consciousness, is another critical symptom. A rapid or irregular heartbeat may also indicate an allergic reaction. If any of these symptoms are present after a tarantula bite, it is vital to call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room immediately. Quick medical intervention, such as the administration of epinephrine, is essential to prevent serious complications and ensure the patient’s safety.
Signs of Infection
Signs of infection after a tarantula bite also require immediate medical attention. Although tarantula bites themselves are not usually infected, the puncture wound created by the fangs can become infected if not properly cleaned and cared for. Increased pain, swelling, and redness at the bite site are common signs of infection. Pus or drainage from the wound is another clear indicator of infection. Fever, chills, and body aches are signs that the infection has spread beyond the bite site. Red streaks radiating from the bite site can indicate that the infection is spreading through the lymphatic system. Any of these symptoms require medical evaluation and treatment. A healthcare professional can assess the infection, prescribe antibiotics, and provide guidance on wound care to ensure proper healing and prevent the infection from spreading. Early intervention is critical to prevent complications and promote a full recovery.
Long-Term Care and Recovery
Long-term care and recovery after a tarantula bite is a crucial aspect of ensuring a full and complete return to health. Even after the initial symptoms have subsided and the immediate danger has passed, there are steps that can be taken to promote healing, prevent future complications, and address any lasting effects. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines can make a significant difference in the quality of recovery. Proper long-term care involves not only treating the physical symptoms but also addressing any psychological or emotional impacts that the experience might have caused. The following steps provide a detailed look at how to ensure a comprehensive and successful recovery from a tarantula bite.
Regularly monitoring the bite site is essential during the recovery period. Examine the area for any signs of recurring or new symptoms, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, or discharge. If any of these symptoms appear, consult a medical professional for guidance. Continue to keep the area clean and dry, as this helps to prevent infection and promote healing. Avoid activities that could irritate the bite site, such as scratching or applying harsh chemicals. If the bite site is itchy, use over-the-counter creams or consult a doctor for stronger medications. Additionally, it is important to protect the area from direct sunlight, as this can exacerbate inflammation and slow the healing process. Following these practices will ensure the healing progresses smoothly and prevent further complications.
In some instances, the experience of being bitten by a tarantula might cause anxiety or fear related to spiders or other insects. If these feelings become overwhelming or persistent, it is recommended to seek emotional support. Talking to a therapist, counselor, or support group can provide valuable strategies for managing these emotions and developing coping mechanisms. There are also relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, that can help to reduce anxiety. Learning more about tarantulas and spiders can help to demystify these creatures and reduce fear. Joining a community or online forum where people share their experiences can provide emotional support and a sense of community. Prioritizing emotional health can ensure a complete and healthy recovery from the incident.
Always follow the advice of a healthcare professional during the recovery period. Attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to ensure that the bite is healing properly and that there are no complications. If you have any questions or concerns, do not hesitate to ask your doctor or other medical professional. They can provide personalized guidance and support based on your specific circumstances. Keep a record of your symptoms, treatments, and any changes you experience, as this can be helpful for monitoring your progress and communicating with your healthcare provider. Following professional advice and communicating with your doctor is essential for a smooth recovery and can lead to the best possible health outcomes. Taking these measures will ensure your long-term health and well-being after the incident.
