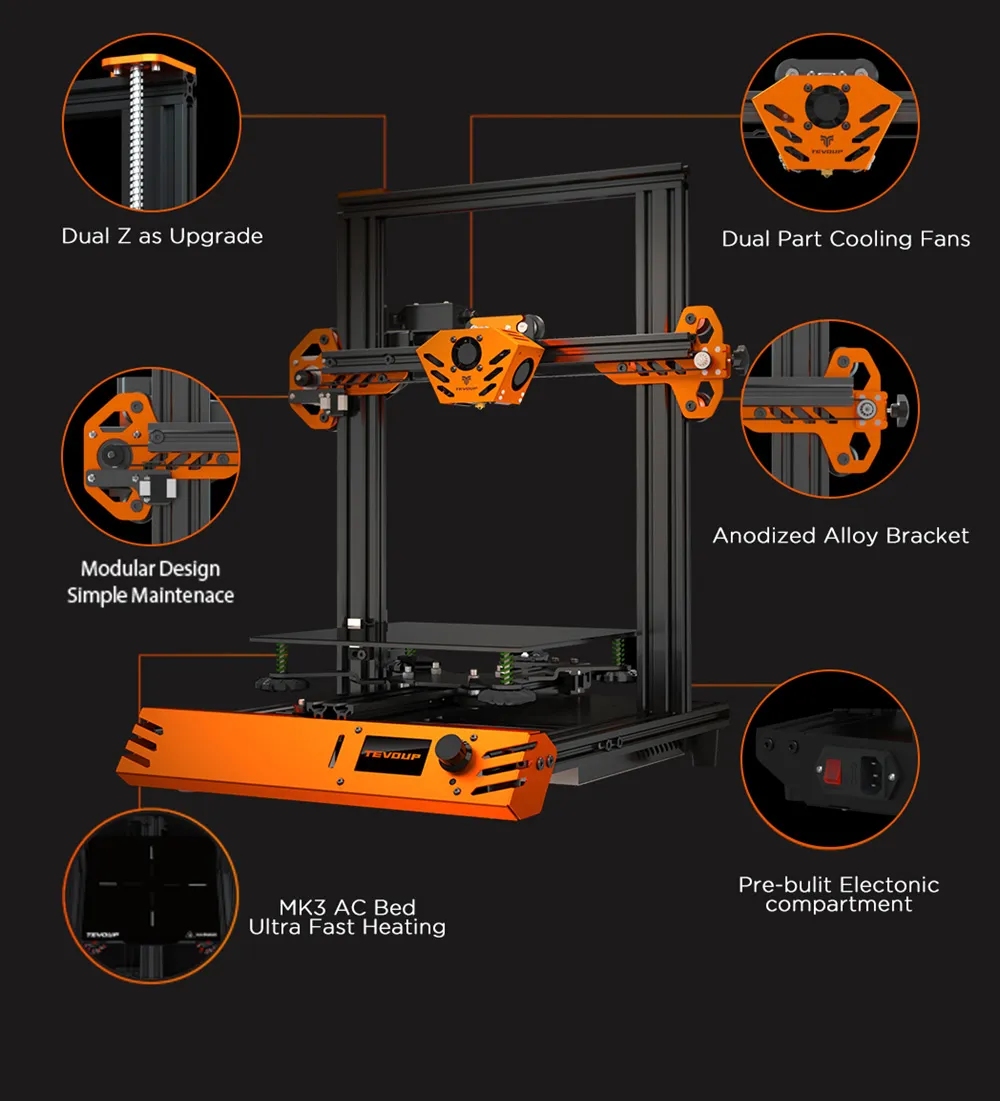
What is 3D Printing Tarantula Software
3D printing tarantula software encompasses a range of applications designed to facilitate the creation of physical objects from digital models using a 3D printer. These software tools are essential for translating digital designs into instructions that a 3D printer can understand and execute. This process involves several key steps, including model preparation, slicing, and generating G-code, the language 3D printers use to control their movements. Without the right software, a 3D printer is essentially useless, as it cannot interpret the design data and convert it into the physical layers that build the object. The software acts as the bridge between the digital world of design and the physical world of 3D printing, making it possible to bring complex and intricate models to life. Whether you are designing a tarantula model or any other object, understanding the role of software is crucial to successful 3D printing.
The Role of Software in 3D Printing
Software is the backbone of the 3D printing process, enabling users to create, modify, and prepare 3D models for printing. It allows for the manipulation of designs, ensuring they are optimized for the 3D printing process. This includes adjusting scale, orientation, and adding support structures. Software also plays a vital role in converting the digital model into a format that the 3D printer can understand. This process, known as slicing, divides the 3D model into thin layers and generates instructions for the printer to deposit material layer by layer. Moreover, the software manages the printer’s settings, such as temperature, speed, and material flow, to ensure the successful printing of the tarantula model or any other design. Effective software choices can significantly improve the print quality, reduce errors, and optimize printing time.
Types of 3D Printing Software

There are several types of software involved in the 3D printing process, each serving a unique purpose. The main categories include CAD software, which is used for designing the 3D models; slicing software, which converts the designs into printer-ready instructions; and control software, which manages the printer’s operations during the printing process. These software types work together to transform an idea into a physical object. The choice of software depends on the user’s skill level, the complexity of the design, and the specific requirements of the 3D printer. Many software packages combine multiple functionalities, offering an all-in-one solution for designing, preparing, and printing 3D models. Understanding the different types of software is vital to streamlining the 3D printing workflow and achieving desired results.
Slicing Software
Slicing software is a critical component in the 3D printing workflow. It takes the 3D model, which is typically in a format like STL or OBJ, and slices it into thin, horizontal layers. Each layer represents a cross-section of the object that the 3D printer will print. The slicing software then generates the G-code, a set of instructions that tells the printer how to move, when to extrude material, and at what temperature. Users can adjust settings within the slicing software, such as layer height, infill density, and support structures, to control the print quality and material usage. Popular slicing software options include Cura, PrusaSlicer, and Simplify3D, each offering a range of features and settings to optimize the printing process. Selecting the right slicing software is crucial for achieving high-quality 3D prints.
CAD Software
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create and modify 3D models. These models are the foundation for anything you want to 3D print, including your tarantula design. CAD software allows users to design objects from scratch or modify existing designs. It provides tools for creating shapes, assembling components, and adding details. There are various CAD software options available, ranging from free, user-friendly programs like Tinkercad to professional-grade software like Fusion 360, SolidWorks, and AutoCAD. Choosing the right CAD software depends on your design experience and the complexity of the models you intend to create. CAD software is essential for those who wish to design their own 3D models or customize existing ones for 3D printing.
Control Software

Control software, also known as printer firmware or host software, is the interface used to manage the 3D printer’s operations during the printing process. It communicates with the printer to send the G-code instructions generated by the slicing software. This software allows users to monitor the print progress, adjust settings such as print speed and temperature, and control the printer’s movements. Some control software packages also offer advanced features like remote monitoring and control via Wi-Fi or Ethernet. Examples of control software include Repetier-Host, OctoPrint, and the software integrated directly into the 3D printer. The control software ensures the printer follows the instructions accurately, resulting in a successful 3D print. It’s the final step in ensuring your tarantula model is printed correctly.
Choosing the Right Software for Your Tarantula
Selecting the right software is crucial for a smooth and successful 3D printing experience, especially when creating complex designs like a tarantula model. The choice depends on several factors, including your experience level, the complexity of the design, and the specific requirements of your 3D printer. Beginner-friendly software like Tinkercad or Cura are often suitable for those just starting, while more advanced users might prefer Fusion 360 or Simplify3D. It is important to consider the software’s compatibility with your printer, the available features, and the community support available. Doing your research and testing different software options is recommended to find the best fit for your specific needs and the intricacies of your 3D printing project.
Compatibility Considerations
Compatibility is a critical factor when choosing 3D printing software. Ensure that the software you select is compatible with your 3D printer’s firmware and hardware. Check the software’s system requirements to make sure your computer meets the necessary specifications. Furthermore, verify that the software supports the file formats your 3D printer can read. Most printers accept STL files, but other formats like OBJ and 3MF might also be supported. Compatibility issues can lead to printing errors or the inability to print at all. Reading user reviews and checking the software’s documentation can help you determine if it is compatible with your printer and other existing software.
Ease of Use
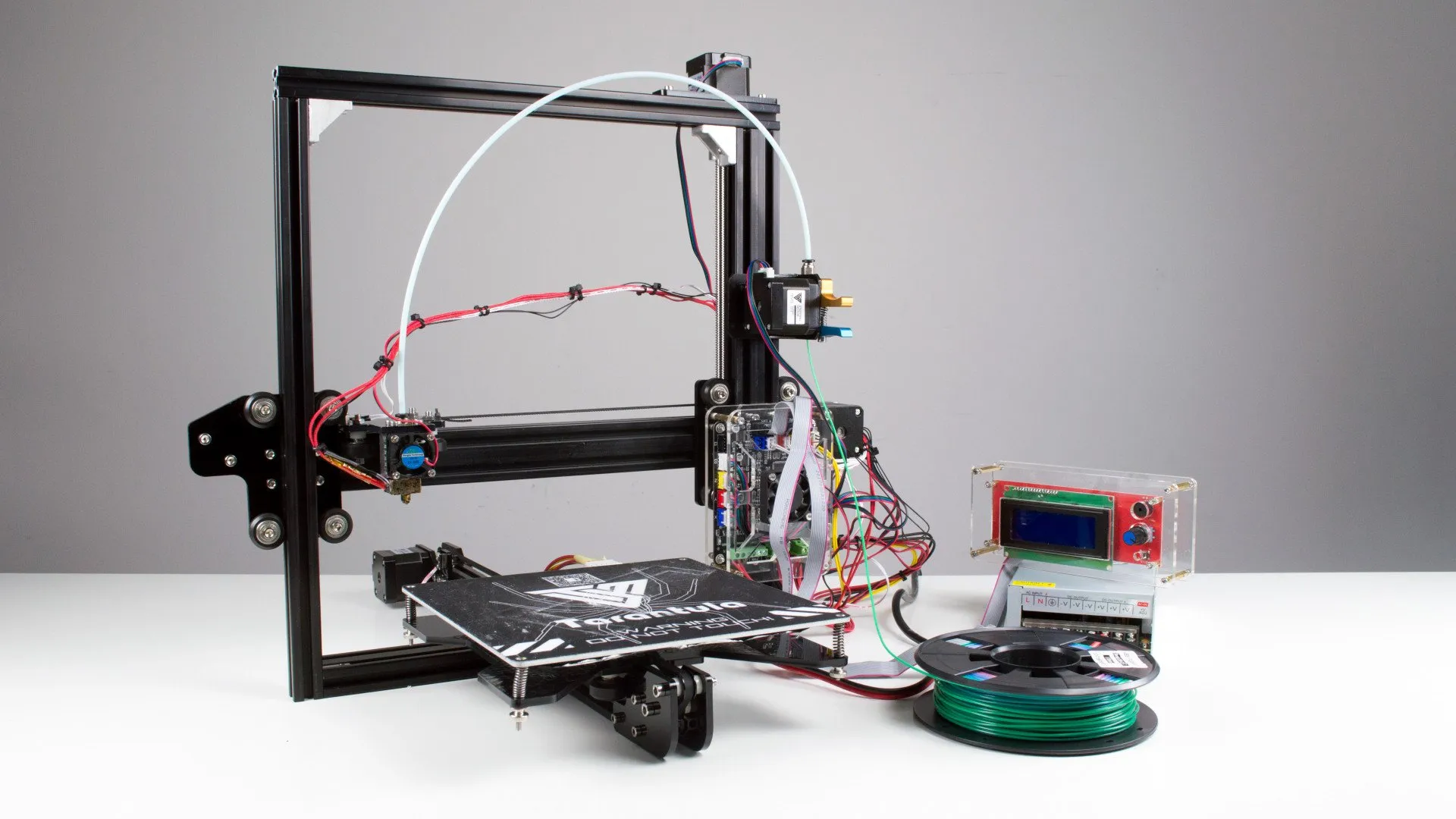
Ease of use is another important consideration when selecting 3D printing software. Consider the user interface and whether it is intuitive and easy to navigate, especially if you are a beginner. Some software packages offer a simplified interface with basic settings, while others provide advanced controls for experienced users. Look for software with clear instructions, tutorials, and community support. Many software programs have online resources, such as forums and tutorials, that can help you troubleshoot problems and learn how to use the software effectively. Starting with user-friendly software can significantly reduce the learning curve and make the 3D printing process more enjoyable, especially for complex designs like a tarantula.
Advanced Features
For experienced users, advanced features in 3D printing software can provide greater control over the printing process. These features might include advanced support structure customization, detailed control over print settings, and the ability to simulate the print before starting. Some software offers features like multi-material printing and remote monitoring capabilities. If you plan to print complex models or require high precision, consider software with advanced features that allow for fine-tuning settings and optimizing the print. Investing time to understand these advanced options can significantly improve print quality, speed, and material usage. Evaluate your project’s complexity and your own skill level when deciding whether you need advanced features.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using 3D Printer Tarantula Software
Using 3D printing software involves a series of steps to prepare and print a 3D model, such as a tarantula. The process typically includes installing and setting up the software, loading and preparing the model, slicing the model, generating G-code, and finally, uploading and printing the design. Each step is crucial to the overall success of the 3D printing project. This guide will walk you through the essential steps, ensuring you understand each process and can apply it to your own 3D printing projects. Following these steps correctly helps achieve high-quality prints and reduces the chances of printing errors. This step-by-step approach is essential, especially for intricate models like the tarantula.
Installing and Setting Up the Software

The first step is to install and set up the necessary 3D printing software on your computer. Download the software from a trusted source and follow the installation instructions. During setup, you might need to configure the software for your specific 3D printer model. This involves selecting your printer from the list of supported devices and setting the printing parameters, such as the bed size and nozzle diameter. Ensure the software is updated to the latest version to benefit from new features and bug fixes. Proper software setup ensures your printer communicates effectively with the software and that your prints are executed according to your intended parameters. Careful setup is critical for a successful 3D printing experience, especially for a detailed model like a tarantula.
Loading and Preparing Your Tarantula Model
Once the software is installed and set up, the next step is to load your tarantula model. Import the model file, which is typically in STL or OBJ format, into the software. You might need to scale, rotate, and position the model on the virtual build plate to ensure it fits within the printer’s build volume and is oriented correctly for printing. Adjusting the model’s orientation is important for optimizing support structures and print quality. The software allows you to make these adjustments before slicing. Examine the model carefully for any defects or issues that might affect the print, and consider making corrections if necessary. Preparing the model properly is a crucial step toward ensuring a high-quality print of the tarantula.
Slicing the Model
Slicing is the process of converting your 3D model into a series of layers that the 3D printer can understand. In the slicing software, you will configure various settings, such as layer height, infill density, print speed, and support structures. Layer height affects the detail and smoothness of the print; a lower layer height results in finer details but takes longer to print. Infill density determines how solid the interior of the model will be, affecting its strength and material usage. Support structures are generated to support overhanging parts of the model during printing. Optimizing these settings is crucial for achieving the desired print quality and reducing material waste. After configuring the settings, the software slices the model and generates G-code.
Generating the G-code

After slicing, the software generates G-code, a set of instructions that tells the 3D printer how to move, extrude material, and control the print settings. This G-code is specific to your 3D printer and the chosen settings. The software translates the sliced layers into a series of commands that the printer will execute. The generated G-code includes information about the path of the print head, the amount of material to extrude, the temperature of the nozzle and bed, and the print speed. Reviewing the G-code can help you identify potential issues before printing, such as unexpected movements or settings. Once the G-code is generated, it’s ready to be uploaded to the 3D printer for printing.
Uploading and Printing
The final step involves uploading the G-code to your 3D printer and starting the print. This can typically be done via an SD card, USB connection, or Wi-Fi, depending on your printer’s capabilities. Once the G-code is uploaded, the printer will begin to execute the instructions. Monitor the print progress and check for any issues, such as warping, delamination, or nozzle clogs. Adjust the printer settings as needed during the print process to optimize results. When the print is complete, carefully remove the model from the build plate and remove any support structures. Inspect the finished print for any imperfections. Your printed tarantula model should be complete and ready.